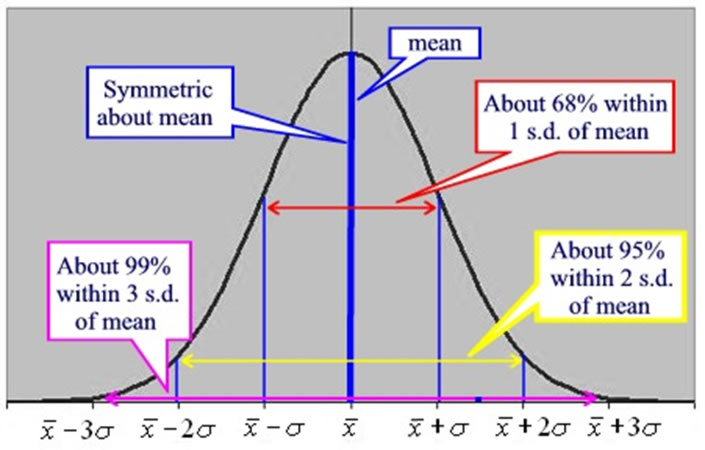
A characteristic property of the normal distribution is that 68% of all of its observations fall within a range of ±1 standard deviation from the mean, and a range of ±2 standard deviations includes 95% of the scores. In other words, in a normal distribution, observations that have a standardized value of less than -2 or more than +2 have a relative frequency of 5% or less.
Standardized value means that a value is expressed in terms of its difference from the mean, divided by the standard deviation and it is this basic computation that enables ALL normal distributions to be compared to one another.